The following are selected questions from slides that the instructors said might appear in the exams. I think these questions are important and should be reviewed for one time at least. For some questions, I asked ChatGPT to answer it.
- What is the role of the scoping phase in the experimental process? Create the foundation for the experiment; Define intentions for the experiment; Increase the probability of success.
- How does the GQM framework help in the research process? Goal Definition: It starts with setting clear goals which outline the purpose of measurement and what is to be achieved. Question Design: Based on the goals, research questions are formulated. These questions aim to narrow down the focus to specific areas of interest that need to be investigated to achieve the goals. Metric Selection: For each question, specific metrics are identified that can provide the data needed to answer the questions. This selection process ensures that the data collected is relevant and useful for the research objectives.
2.3 Controlled Experiment 2
 Four types of validity:
external: sample should generalize to whole population
internal: minimize bias (like control variables)
-adopting a within-subject design with a random assignment of subjects to the groups
conclusion: whether there is a relationship between the treatment and the outcome (lack of statistical power will post a threat)
construct: the degree to which inferences can legitimately be made from the operation to the theory, e.g.:
-experimental design problems will post a threat
-whether the right metrics were used to investigate the comprehensibility of risk models
#validity
Four types of validity:
external: sample should generalize to whole population
internal: minimize bias (like control variables)
-adopting a within-subject design with a random assignment of subjects to the groups
conclusion: whether there is a relationship between the treatment and the outcome (lack of statistical power will post a threat)
construct: the degree to which inferences can legitimately be made from the operation to the theory, e.g.:
-experimental design problems will post a threat
-whether the right metrics were used to investigate the comprehensibility of risk models
#validity



2.5 Analysis and Interpretation 1
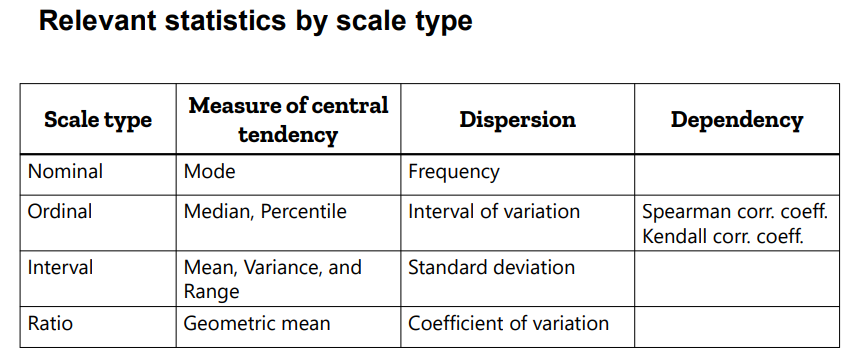
- What are three key measurements used in descriptive statistics to assess data distribution?
mean, median, mode
- Why does analyzing data with numerous features pose challenges, and what methods can we use to address these challenges?
Curse of Dimensionality, Overfitting, Computational Intensity, Correlation vs. Causation…

- What are the statistical assumptions before we test a hypothesis? Why is it important to consider and maintain statistical assumptions in our analyses?

2.6 Analysis and Interpretation 2 ⭐
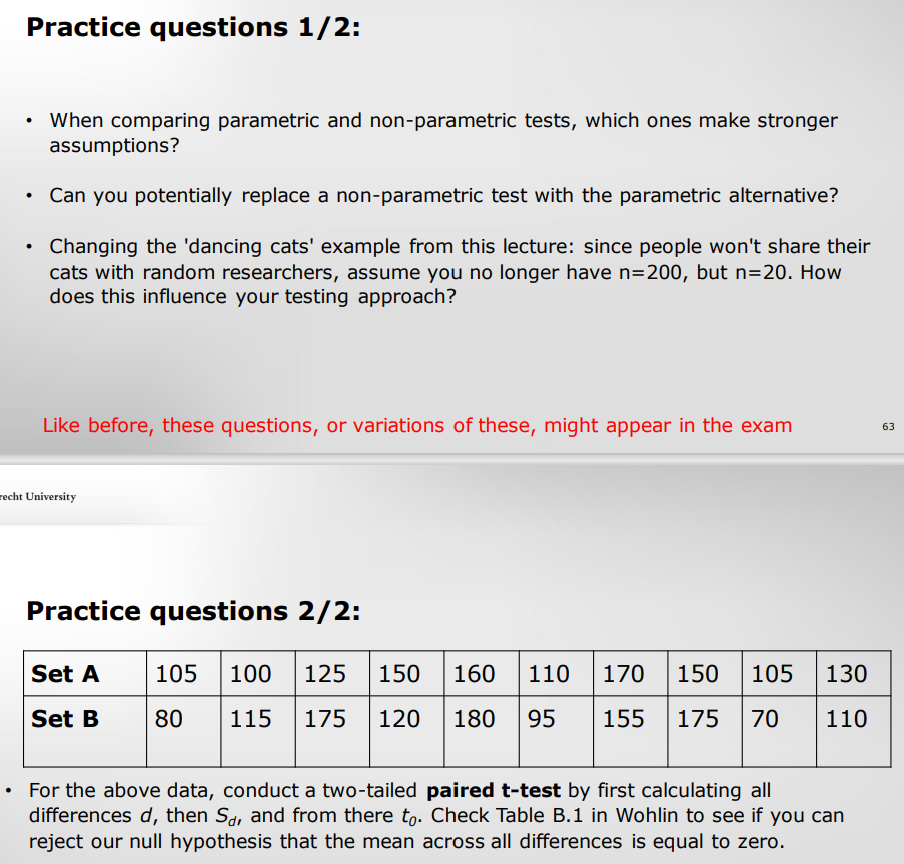
 parametric test is more valid, But if the sample is to small, non-parametric is more suitable.
parametric test is more valid, But if the sample is to small, non-parametric is more suitable.
I found the slides are different from YouTube tutorials. The slides said chi-squared tests are used in binomial tests, but YouTube tutorials said they are used between categorical variables. Just believe what you think make sense.😂
2.7 Systematic Literature Review & Peer Review
- What kind of scientific literature sources exist?
- What ways to search for literature exist?
- What ways to publish literature exist?
- How do reviewing processes differ between a conference and a journal?

- What is the difference between a blind and a double-blind reviewing?
- Under which circumstances is design science suitable as a methodology for research projects? When a scientific project serves a purpose that is defined by stakeholders from a social context (people have a goal, but don’t know how to fulfill it), then science can help to reach that goal. In order to do so, science needs a knowledge context (because you can’t design something reasonable without knowing about it). The knowledge context is the scientific community and the literature that exist about topics. When both types of contexts are relevant in a project, then it makes sense to refer to it as a design science project.
- How does design science take care that a project is not just a consultant activity? This connects to the above and emphasizes that only a reasonable balance between benefiting the social context and the knowledge context makes a good design science project. Relevance refers to serving the social context, rigor to interacting with the knowledge context. To be rigorous means to apply methods, write scientific papers about the project, go to conferences, publish in journals… In other words: to do research as part of the project.